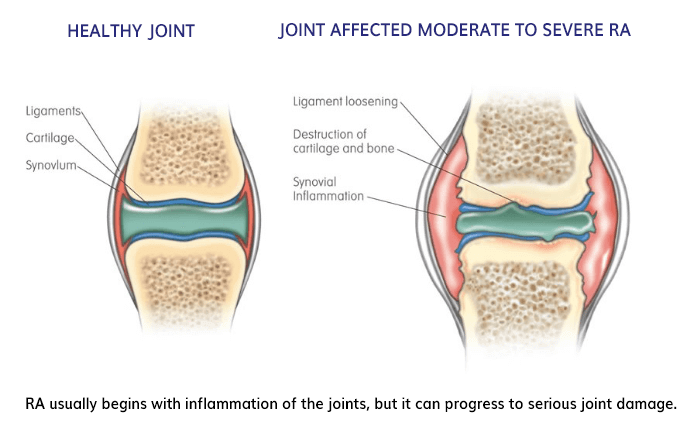
Arthritis is not a single disease but rather an umbrella term that encompasses over 100 different conditions. The most common types of arthritis include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease caused by wear and tear of the joint cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that targets the joints. Gout, on the other hand, is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints.

Causes and Risk Factors:
The causes of arthritis vary depending on the type. Osteoarthritis is primarily caused by aging, joint injury, obesity, and repetitive stress on the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is believed to be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, leading to an immune system malfunction. Gout is often associated with an excessive intake of purine-rich foods, leading to increased uric acid levels in the body.
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing arthritis. These include age, gender (women are more prone to rheumatoid arthritis), family history, obesity, previous joint injuries, and occupations involving repetitive joint movements.
Common Symptoms:
While the symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity, some common signs include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. Individuals with arthritis may also experience fatigue, loss of appetite, and a general feeling of malaise. Symptoms can worsen over time if not properly managed, leading to a significant impact on daily activities and overall quality of life.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options:
Early diagnosis is crucial for effectively managing arthritis. Medical professionals typically use a combination of methods, including medical history review, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies such as X-rays or MRIs, to determine the type and extent of arthritis.
Treatment options for arthritis focus on alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and improving joint function. Non-pharmacological interventions include weight management, physical therapy, heat/cold therapy, and assistive devices. Medications such as analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
In severe cases, surgical interventions such as joint replacement or joint fusion may be considered. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and avoiding excessive alcohol and tobacco consumption can greatly improve the overall well-being of individuals with arthritis.
Living with Arthritis:
Living with arthritis requires a comprehensive approach to manage symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. This includes staying active with low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that exacerbate joint pain. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also help manage stress and improve mental well-being.
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor the progression of arthritis and adjust treatment plans as needed. Support from family, friends, and arthritis support groups can also provide emotional support and a platform to share experiences and coping strategies.
Conclusion:
Arthritis is a prevalent condition affecting millions of people worldwide. It refers to a group of joint disorders characterized by inflammation, stiffness, and pain. While arthritis can affect individuals of all ages, it becomes more common as people age. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of arthritis, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. By understanding this condition better, you can take proactive steps towards managing arthritis and improving your quality of life.